
Indexing is the foundation of SEO. Without proper indexing, your website’s pages won’t appear in Google Search results, no matter how well-optimized they are. Unfortunately, Google indexing issues are common and can arise due to technical errors, misconfigurations, or content problems. These issues can prevent your pages from being crawled, indexed, and ranked, ultimately hurting your site’s visibility and traffic.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive deep into how to fix page indexing issues using Google Search Console. We’ll cover common indexing problems, step-by-step solutions, and advanced strategies to ensure your site is fully indexed and optimized for search engines. Whether you’re dealing with 404 errors, robots.txt blocks, or soft 404s, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and tools to resolve these issues effectively.
Why Indexing Issues Matter
Indexing is the process by which Google crawls and adds your web pages to its search database. If your pages aren’t indexed, they won’t appear in search results, leading to lost traffic, reduced conversions, and lower revenue. Common reasons for indexing issues include:
-
Technical errors (e.g., server issues, redirect loops).
-
Misconfigured settings (e.g.,
noindextags, robots.txt blocks). -
Content problems (e.g., duplicate content, thin content).
By addressing these issues, you can improve your site’s search performance and ensure your content reaches your target audience.
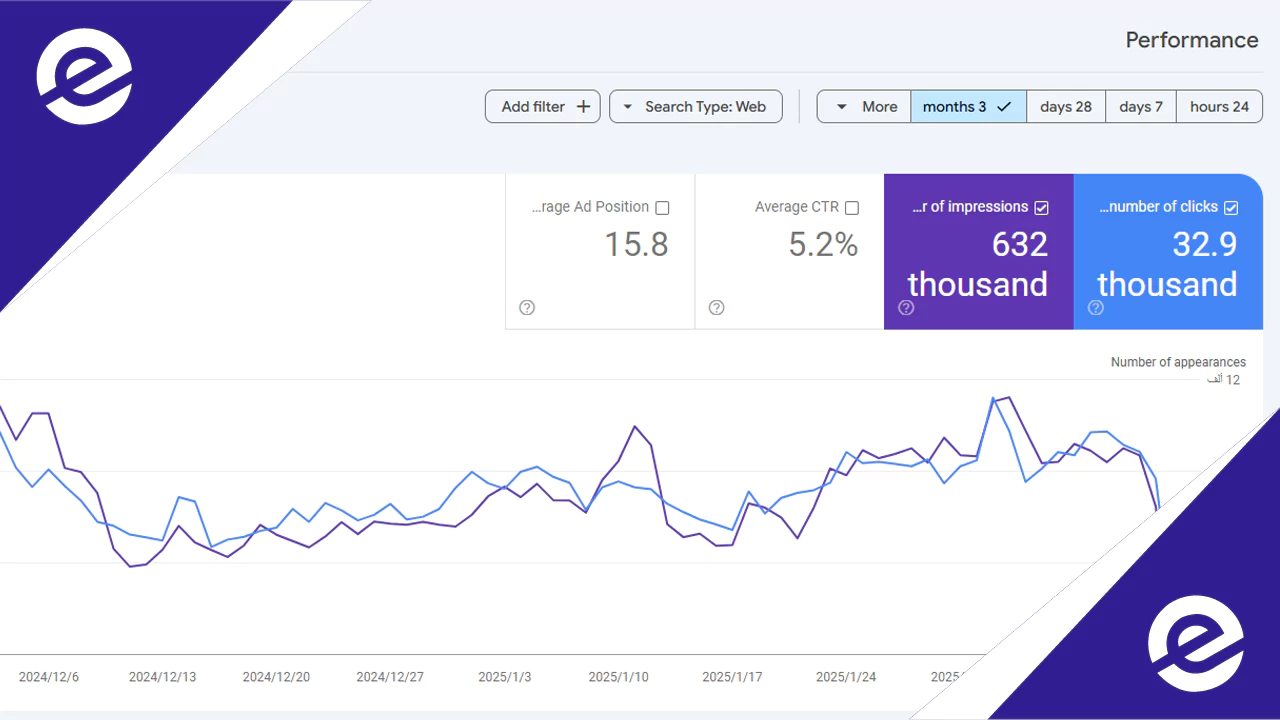
Common Google Indexing Issues and How to Fix Them
1. Not Found (404) Errors
A 404 error occurs when Googlebot tries to access a page that no longer exists. This can happen due to broken links, deleted pages, or incorrect URLs.
How to Fix:
-
Redirect the URL: Use a 301 redirect to point the old URL to a relevant page. This ensures users and search engines are directed to the correct content.
-
Fix broken links: Use tools like Screaming Frog or Ahrefs to identify and update internal and external links pointing to the broken URL.
-
Create a custom 404 page: Design a user-friendly 404 page that guides visitors to helpful content on your site.
Pro Tip: Regularly audit your site for broken links using tools like Ahrefs or SEMrush to prevent 404 errors from occurring.
2. Excluded by ‘noindex’ Tag
If a page has a noindex tag, Google won’t index it. This can happen unintentionally due to plugin settings, theme configurations, or CMS errors.
How to Fix:
-
Remove the
noindextag: Edit the page’s HTML or CMS settings to remove thenoindexdirective. -
Check plugins and themes: Ensure they aren’t adding
noindextags to your pages. For example, some SEO plugins may applynoindexto archive or tag pages by default.
Pro Tip: Use the Google Search Console URL Inspection Tool to check if a page is excluded due to a noindex tag.
3. Blocked by robots.txt
The robots.txt file can block Googlebot from crawling specific pages. If these pages are essential, they won’t be indexed.
How to Fix:
-
Edit robots.txt: Remove or modify the
Disallowdirective for the affected pages. For example, changeDisallow: /example-page/toAllow: /example-page/. -
Test changes: Use the Google Search Console robots.txt tester to verify the updates and ensure Googlebot can access your pages.
Pro Tip: Avoid blocking CSS and JavaScript files in robots.txt, as this can prevent Googlebot from rendering your pages correctly.
4. Redirect Errors
Redirect errors occur when Googlebot encounters broken or improperly configured redirects, such as redirect chains or loops.
How to Fix:
-
Simplify redirects: Ensure each redirect points directly to the final destination. Avoid creating long chains of redirects.
-
Avoid redirect loops: Check for circular redirects where a page redirects back to itself.
-
Use 301 redirects: Replace temporary (302) redirects with permanent ones to signal to Google that the change is permanent.
Pro Tip: Use tools like Screaming Frog to identify and fix redirect chains and loops.
5. Soft 404 Errors
A soft 404 occurs when a page returns a 200 status code (indicating success) but lacks meaningful content. This can confuse Googlebot and prevent indexing.
How to Fix:
-
Add relevant content: Ensure the page provides value to users. For example, if a product page is out of stock, add a message explaining when it will be available.
-
Return a 404 status code: If the page is invalid, configure it to return a proper 404 response.
Pro Tip: Use the Google Search Console Index Coverage Report to identify pages with soft 404 errors.
6. Server Errors (5xx)
Server errors (e.g., 500, 502, 503) occur when Googlebot can’t access your site due to server issues. These errors can prevent Google from crawling and indexing your pages.
How to Fix:
-
Check server logs: Identify and resolve the root cause of the error. Common issues include server overload, misconfigured plugins, or database errors.
-
Contact your hosting provider: If the issue persists, seek technical support from your hosting provider.
Pro Tip: Monitor your site’s uptime using tools like UptimeRobot to detect and resolve server errors quickly.
Tools to Diagnose and Fix Indexing Issues
1. Google Search Console
-
Index Coverage Report: Identifies pages with indexing issues and provides detailed error descriptions.
-
URL Inspection Tool: Checks the indexing status of specific URLs and allows you to request re-indexing.
2. Third-Party Tools
-
Screaming Frog: Crawls your site to identify technical SEO issues, including redirect chains, broken links, and missing meta tags.
-
Ahrefs: Monitors your site’s indexability and identifies pages blocked by robots.txt or
noindextags. -
Google Index Checker: Use tools like SmallSEOTools to check if your pages are indexed by Google.
How to Request Indexing in Google Search Console
If you’ve fixed an indexing issue, you can request Google to re-crawl and re-index your pages:
-
Open Google Search Console.
-
Use the URL Inspection Tool to check the affected page.
-
Click Request Indexing to submit the page for re-indexing.
Pro Tip: After submitting a Google Search Console indexing request, monitor the page’s status in the Index Coverage Report to ensure it’s indexed correctly.
Advanced Strategies to Prevent Indexing Issues
1. Submit a Sitemap
A sitemap helps Google discover and index your pages more efficiently. Submit an XML sitemap via Google Search Console to ensure all your pages are crawled.
2. Optimize Crawl Budget
Crawl budget refers to the number of pages Googlebot can crawl on your site within a given time. To optimize crawl budget:
-
Fix broken links and redirects.
-
Remove low-value pages.
-
Use internal linking to guide Googlebot to important pages.
3. Use Canonical Tags
Canonical tags help prevent duplicate content issues by indicating the preferred version of a page. For example, if you have multiple URLs for the same product, use a canonical tag to point to the main product page.
4. Monitor Indexing Status
Regularly check your site’s indexing status using tools like Google Search Console and Ahrefs. Address any issues promptly to maintain optimal search performance.
Conclusion
Fixing Google indexing issues is essential for maintaining your site’s visibility and SEO performance. By using tools like Google Search Console and following the steps outlined above, you can resolve common issues and ensure your pages are indexed correctly.
For more detailed guides, visit:
Best Web Hosting Services in 2025



